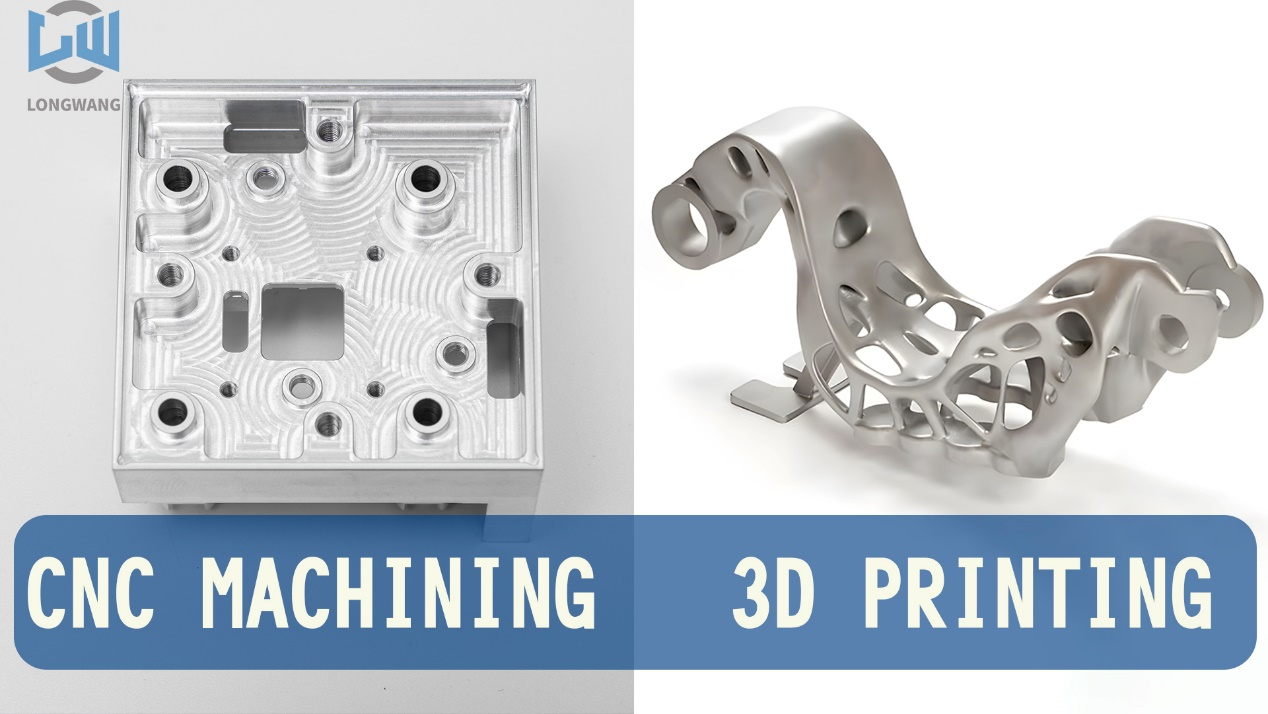
3D Printing vs. CNC Machining: Which is Better for Prototyping and End-Use Parts?
In today’s manufacturing landscape, both 3D printing and CNC machining play critical roles in prototyping and producing end-use parts. At Dongguan Longwang Hardware, we leverage both technologies to deliver precision components. But how do you choose between them? Let’s break down their strengths and limitations.
1. Technology Overview
· 3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing)
Builds parts layer-by-layer using materials like plastics, resins, or metals. Ideal for complex geometries and rapid iterations.
· CNC Machining (Subtractive Manufacturing)
Cuts material from solid blocks (metal, plastic, wood) to create high-precision parts. Best for tight tolerances and durable components.
2. Prototyping: Speed vs. Precision
Factor
3D Printing
CNC Machining
Speed
1-3 days (ideal for quick iterations)
3-7 days (setup-intensive)
Cost
Low for small batches
Higher for complex designs
Design Flexibility
Excellent for organic shapes
Limited by tool accessibility
Example: A client needed 10 prototype parts in 48 hours. 3D printing with nylon PA12 met their deadline, while CNC would have required costly tooling changes.
3. End-Use Parts: Material & Durability
· 3D Printing
✔️ Lightweight aerospace components
✔️ Custom medical implants
❌ Limited strength vs. CNC parts
· CNC Machining
✔️ Automotive engine components
✔️ High-stress industrial tools
❌ Higher material waste
4. Cost Analysis
· <500 units: 3D printing often cheaper
· >1,000 units: CNC machining gains economies of scale
Case Study: A drone manufacturer saved 35% by using 3D printing for 300 custom housings but switched to CNC for 5,000+ production runs.
5. When to Choose Each Technology
Opt for 3D Printing if:
· You need <100 complex parts
· Design changes are frequent
· Weight reduction is critical
Choose CNC Machining when:
· Tolerance <0.1mm is required
· Production volumes exceed 500 units
· Parts face high mechanical stress
Conclusion
At Dongguan Longwang Hardware, we recommend:
1. Use 3D printing for fast prototyping and low-volume complex parts.
2. Switch to CNC machining for high-precision, high-volume production.
Need help deciding? Contact our engineers for a free project evaluation!